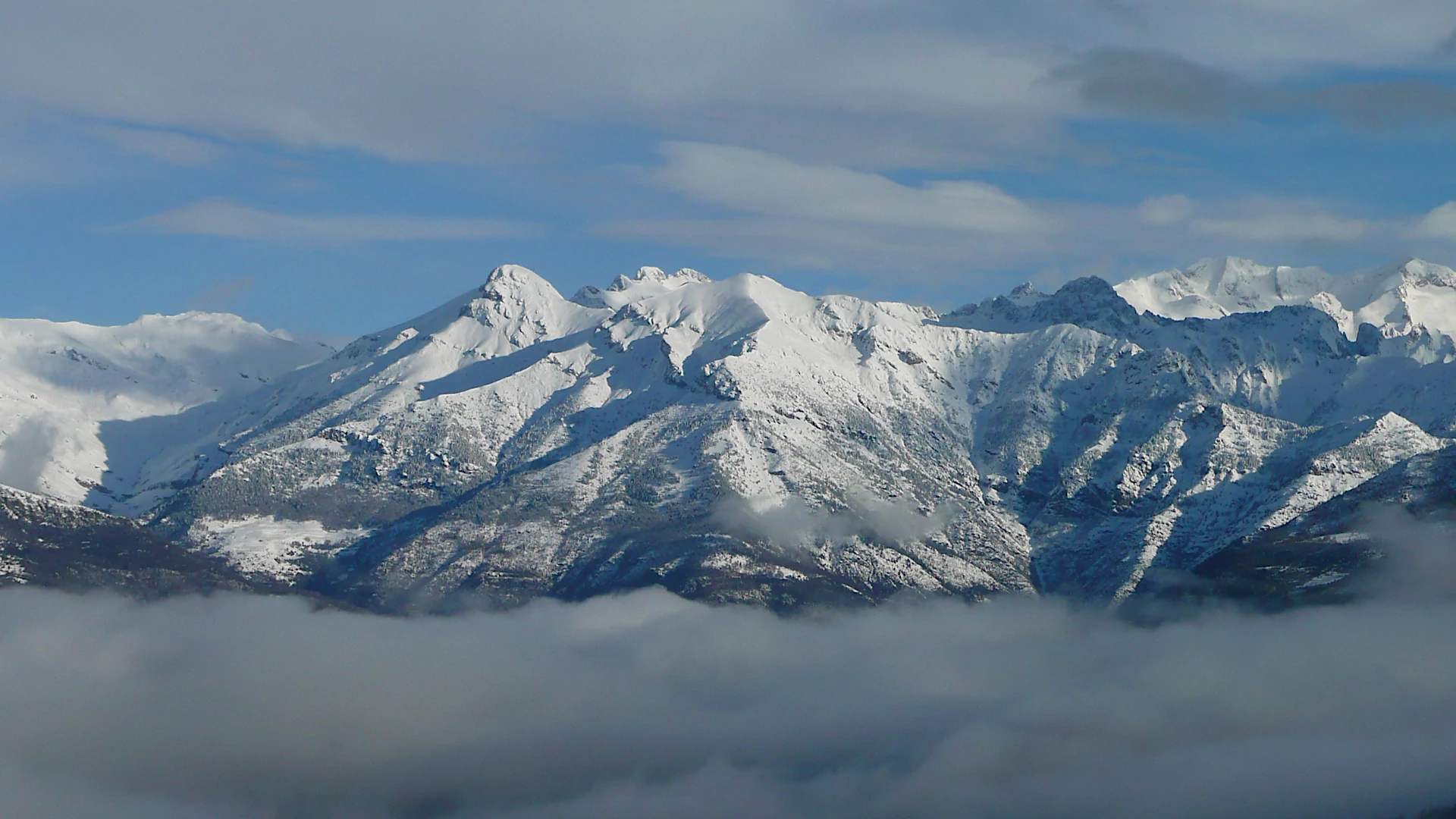
The park was declared on June 23, 1994, with an area of 33,267 ha, with the aim of protecting its natural values, vegetation, flora, landscapes and geomorphological formations, preserve and enhance ecosystems and ensure the rational use of its natural resources. It extends over the head of the three eastern valleys of the Aragonese Pyrenees: the Barrabés to the east, and shared border between Catalonia and Aragon, Benasque in the center and Chistau to the west. Rivers Noguera Ribagorzana, Esera and Cinqueta drain respectively these valleys, flanked and crowned by the largest group of "three thousand" in the Pyrenees: Aneto (3.404m), Maladeta (3.308m), Posets (3.375m) and Perdiguero (3.221m ).
Over 70% of the Natural Park has elevations above 1,800 meters, is of great interest in their ways of modeling glacier, the mountain lakes and karst phenomena. Within its boundaries are three natural monuments of the Pyrenean glaciers: Macizo de la Maladeta, Macizo de Perdiguero and Macizo de Posets.
The Park offers numerous activities for all tastes and seasons, highlighting the activities of climbing, hiking and skiing mountain. It also hosts a network of refuges that are strategically located: Angel Orús shelter in the Eriste Valley, Estós shelter in the Estós Valley, Cap de Llauset in Barrabès Valley, the Renclusa shelter on the north side of Aneto and Biadós shelter in the Chistau Valley.
|
|
It extends over the head of the three eastern valleys of the Aragonese Pyrenees. |

.JPG)